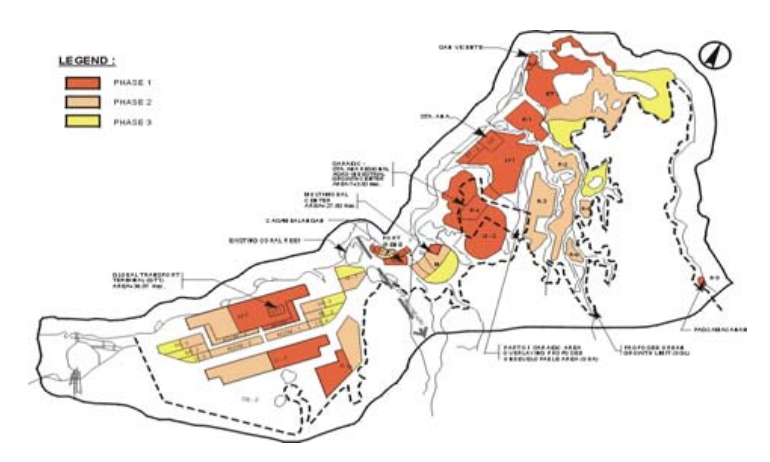


The Cagayan Special Economic Zone and Freeport (referred to as the “Zone”) was defined by RA 7922, which was enacted on February 24, 1995. Situated in the northeastern part of Luzon Island, the Zone offers convenient accessibility to Southeast Asia, Taiwan, the China Mainland, Japan, and the United States’ west coast. Among the total land area of 54,000 hectares that constitute the “Zone,” approximately 23% are designated as potential sites for urban, sub-urban, and agro-industrial development. However, these areas are subject to limitations due to the presence of steep surrounding slopes, protected forests and watersheds, and other environmentally sensitive regions.
The principal development nodes consisted of an integrated agro-industrial area complex comprising of:
- Agro-industrial producing and processing enclaves that will match local agro-livestock producers with foreign investment and technology;
- Light industrial parks that will handle light industrial assembly and production of consumer goods such as garments furniture, handicrafts, etc.;
- Medium-scale industrial parks that will handle processing of such products as electronics, computer parts manufacturing, downstream support industries, etc.; and
- Parks for heavy but environmentally friendly industries such as shipbuilding and repair, aircraft and automotive engine and parts manufacturing, etc.
The following major industrial development thrust was complemented by:
- Support commercial and recreational centers;
- Institutional and government centers which will include specialized training and processing centers;
- Residential areas for local residents, production workers, middle management employees, and corporate/factory executives.
- Eco-tourism belt which will consist of a marina, beach resorts, theme parks, water sports recreational areas, a casino complex and a golf course and country club.
Support infrastructure development:
- An efficient power supply source on wholesale basis from the NPC initially but eventually from its own power sub-stations;
- A sufficient water supply from a very prolific watershed system that
- will provide surface and underground water sources at certain strategic points;
- State-of-the-art telecommunications and electronic data interchange facilities with comprehensive electronic commerce capabilities;
- Sewerage systems and waste treatment plants for liquid and solid wastes; and
- A world-class multi-modal circulation system consisting of wide and inter-connected road systems and a railway facility that will connect airport and seaport to industrial parks, commercial and residential suburbs and eventually to the agro-production hubs in the lower Cagayan Valley southward and to the Ilocos Region westward.
PROJECT SCOPE
- Phase I – Master Development Plan
- Phase II – Feasibility Studies
Eight (8) Major Components:
- Airport
- Seaport – Port Irene
- Housing
- Roads and Drainage
- Power Supply
- Water Supply and Sewerage
- Telecommunications
- Solid Waste Management
